
When you select an infrared heater, you need a clear process to ensure comfort and efficiency. Start by assessing your space and usage patterns, then choose the right heater type for your needs. Calculate the heating power based on room size and layout, and consider essential features such as safety mechanisms and energy efficiency. Review installation requirements and maintenance needs. Matching the infrared heater to your unique environment maximizes performance—infrared heaters consume about 30% less energy than traditional systems, and their elemento calefactor and heating tubes deliver targeted warmth. These factors to consider help you choose the right heater for consistent, cost-effective results.
Understanding Infrared Heaters
How Infrared Heaters Work
You experience warmth from an infrared heater through a process that mimics the sun’s natural heat. Infrared heating uses electromagnetic radiation to transfer energy directly to objects and people in a room. This method does not require air as a medium, so you feel the heat almost instantly after turning on the unit. Infrared heaters generate this energy either electrically or by burning gas. Electric heaters use materials like ceramic or quartz tubes, while gas heaters rely on heated metal plates. The design often includes emitters and reflectors, which focus the infrared radiation toward your space for maximum efficiency.
- Infrared heaters can reach high temperatures, limited only by the materials used in their emitters.
- You benefit from a fast response time, often within 1–2 seconds.
- The heating remains non-contact, so it does not disturb objects or air movement.
- Infrared heating systems work well for both stationary and moving targets, making them versatile for many applications.
Note: Infrared heating systems deliver focused warmth, creating temperature gradients that allow you to target specific areas without wasting energy.
Key Benefits of Infrared Heaters
Infrared heating offers several advantages over traditional systems. You gain from high energy efficiency, as electric heaters can convert up to 85% of input energy into usable heat. Gas heaters also provide effective warmth, though with slightly lower efficiency. Recent studies show that combining infrared heating with other methods can reduce energy consumption by over 60% in some applications. You also enjoy rapid heat delivery, which means you do not wait long for comfort.
- Infrared heating systems help lower your energy bills and reduce carbon emissions.
- You can maintain comfort at lower air temperatures, which further cuts costs.
- The technology supports precise control, so you can adjust warmth to your needs.
- Infrared heaters operate quietly and do not circulate dust, making them ideal for allergy-sensitive environments.
Types of Infrared Heaters
You can choose from several types of heaters, each suited to different spaces and needs. Market research divides infrared heaters into portable, wall-mounted, and ceiling-mounted models. Portable units offer flexibility for residential use, letting you move warmth where you need it. Wall-mounted heaters fit well in both homes and businesses, saving floor space. Ceiling-mounted models work best in commercial or industrial settings, where you need to heat large or open areas.
- Portable infrared heaters: Best for flexible, personal heating in homes.
- Wall-mounted infrared heaters: Suitable for both residential and commercial spaces.
- Ceiling-mounted infrared heaters: Designed for larger, open, or industrial environments.
- Both electric heaters and gas heaters are available in these categories, giving you options based on your power source and installation needs.
Tip: When selecting an infrared heating system, match the type of heater to your space and usage patterns for the best results.
Step 1: Identify Your Space and Heating Needs
Selecting the right infrared heater starts with a careful assessment of your space and specific heating needs. You must understand the dimensions, insulation, and how you use each room to ensure efficient and comfortable heating.
Measuring Room Size and Layout
Calculating Square Footage
Begin by measuring the length and width of your room. Multiply these numbers to get the total square footage. For example, a room that is 15 feet long and 12 feet wide has a total area of 180 square feet. This calculation forms the foundation for determining the correct heater size.
Considering Ceiling Height and Open Spaces
Ceiling height plays a significant role in heating efficiency. Standard ceilings are usually 8 feet high, but if your room has higher ceilings, you will need more heating power. Open floor plans or rooms connected to hallways and other spaces require additional consideration. Heat can escape into adjacent areas, so you may need to adjust your calculations.
Tip: Use industry guidelines such as ASHRAE heat loss calculations to size your infrared heating system. Experts recommend sizing the system to 80-90% of the calculated heat loss for optimal comfort and energy savings.
Assessing Insulation and Windows
Insulation quality directly impacts how well your room retains heat. Well-insulated walls and ceilings help keep warmth inside, reducing the workload on your heater. Windows also play a critical role. Research shows that double-pane windows with Low-E coatings significantly reduce heat transfer compared to single-pane options. These features help maintain a stable temperature and improve the efficiency of your infrared heating system. If your room has older or single-pane windows, you may experience more heat loss, which means you should factor this into your heater selection.
Determining Usage Patterns
Think about how you use each room throughout the day. Do you spend most of your time in one area, or do you move between rooms? Spaces used for short periods, such as entryways or workshops, may require a different approach than living rooms or bedrooms where you seek consistent comfort. Consider the time of day you need heating and whether you want to target specific zones or the entire room.
- Identify the primary function of each room.
- Note the times when you need heating the most.
- Decide if you want to heat the whole room or just certain areas.
Placing heaters near colder walls or doors can help address uneven heat loss and improve comfort by reducing cold spots. Positioning heaters to maximize exposure to thermal mass, such as concrete floors, can also help even out temperature distribution.
By carefully evaluating your space, insulation, and usage patterns, you set the stage for selecting an infrared heater that matches your heating needs and delivers reliable performance.
Step 2: Choose the Right Heater Type for Your Space

Selecting the appropriate type of infrared heater ensures you achieve optimal comfort and efficiency in your environment. You must consider the unique requirements of your space, as well as the advantages and limitations of each heater type.
Portable Infrared Heaters
Portable infrared heaters offer flexibility and convenience, making them a popular choice for residential settings or temporary heating needs. You can easily move these units from room to room, allowing you to target specific areas that require warmth. Many homeowners prefer portable models because they combine energy efficiency with user-friendly controls and safety features. These heaters often feature compact designs that fit well in bedrooms, offices, or workshops.
- You benefit from quick setup and minimal installation.
- Portable units suit renters or those who want supplemental heat without permanent changes.
- Modern models often include eco-friendly materials and smart controls for added convenience.
Nota: Portable gas-fired infrared heaters provide both flexibility and ease of use, which is ideal for spaces where permanent installation is not practical.
Wall-Mounted Infrared Heaters
Wall-mounted infrared heaters work well in both residential and commercial spaces. You can install these units at a fixed location, saving valuable floor space and providing consistent, targeted heating. Wall-mounted models often feature sleek, modern designs that blend with your décor. They deliver efficient warmth to living rooms, offices, or even hotel lobbies.
- These heaters offer zoning capabilities, allowing you to heat specific areas without wasting energy.
- Installation is straightforward, and maintenance requirements remain low.
- Many models integrate with smart thermostats, giving you precise control over your heating schedule.
Market analyses show that commercial applications benefit from energy efficiency and the ability to integrate with smart technologies. Regulatory requirements and energy standards also influence the selection of wall-mounted units, especially in public or shared spaces.
Ceiling-Mounted and Panel Infrared Heaters
Ceiling-mounted and panel infrared heaters provide powerful, unobtrusive heating for larger or open areas. You can use these systems in industrial settings, warehouses, or commercial environments where robust construction and high heating capacity are essential. Ceiling-mounted units distribute heat evenly across wide spaces, while panel heaters offer a slim profile that prevents dampness and mold, improving indoor air quality.
- These heaters maximize usable floor space and reduce the risk of accidental contact.
- Installation suits permanent setups in areas with high ceilings or open layouts.
- Technological advancements have introduced models compatible with renewable energy sources and smart controls.
Tip: Always match the heat coverage area of your infrared heater to the size and layout of your space. This ensures efficient operation and prevents energy waste.
When you evaluate your space and heating needs, you can confidently select the right heater type. Infrared heaters offer energy efficiency, low emissions, and practical designs for a wide range of applications.
Commercial and Outdoor Infrared Heaters
You face unique challenges when heating commercial and outdoor spaces. These environments often have large open areas, high ceilings, or exposure to the elements. Standard residential heaters may not deliver the performance you need. Commercial-grade infrared heaters provide targeted, efficient warmth for warehouses, factories, sports facilities, and outdoor patios.
In commercial settings, you often deal with high ceilings and significant heat loss. For example, aircraft hangars and maintenance facilities require powerful radiant systems to maintain comfort. Outdoor spaces, such as restaurant patios or event venues, need heaters that can withstand wind and fluctuating temperatures. You benefit from models designed for durability, weather resistance, and high output.
- You can install ceiling-mounted or wall-mounted units to maximize floor space.
- Outdoor-rated models feature waterproof casings and corrosion-resistant materials.
- Many commercial heaters offer advanced controls for zoning and scheduling.
Tip: For outdoor use, select heaters with an IP rating suitable for your climate. This ensures reliable operation during rain or snow.
Scientific studies show that radiant and conductive heating surfaces must reach higher temperatures than convective systems to maintain comfort in open or drafty environments. Personalized radiant devices, such as overhead panels or leg warmers, help improve thermal sensation and save energy, especially in spaces with low background temperatures. By matching the heater type to the specific demands of your environment, you optimize both comfort and efficiency.
Matching Heater Types to Different Spaces
Choosing the right heater type for each environment ensures you achieve the best results. The following table highlights real-world examples of how organizations matched heater types to their unique needs:
| Environment | Heater Type | Challenge / Issue Identified | Outcome / Benefit of Matching Heater Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rickenbacker Air National Guard Base (Aircraft Hangars) | Low radiant output linear units (initially) | Ineffective heating in high-ceiling hangars; occupant discomfort; roof penetrations causing leaks | Identified mismatch; need for higher output radiant systems suited for aviation hangars |
| Purdue University (Indoor Practice Facility) | Radiant heating systems | Requirement for quiet, unobtrusive, energy-efficient heating | Radiant heat met coaching and engineering needs, enhancing comfort and efficiency |
| Caterpillar Corporate Hangar | Advanced radiant infrared equipment | High standards for quality and performance in corporate jet hangar | Preferred vendor supplying superior radiant heating solutions meeting operational demands |
| L-3 Communications (Maintenance Facility) | Advanced radiant heating systems | Prior vendor’s energy efficiency was inferior | Switched to Advanced Radiant Systems for improved energy efficiency and performance |
You see that each space presents its own set of challenges. For example, high-ceiling hangars need high-output radiant systems, while indoor sports facilities benefit from quiet, efficient radiant panels. Scientific research supports this approach, showing that combining radiant and convective heating can maintain consistent comfort and optimize energy use. You should always assess the specific demands of your environment before selecting a heater.
When you match heater types to your space, you ensure that infrared heaters deliver reliable, cost-effective performance tailored to your needs.
Step 3: Calculate the Required Heating Power for Infrared Heaters
Understanding Wattage and BTUs
When you select an infrared heater, you need to understand two key measurements: wattage and BTUs (British Thermal Units). Wattage measures the electrical power the heater uses, while BTUs indicate the amount of heat the unit can deliver. Most infrared heating systems list both values in their specifications. For residential spaces, you often see wattage ratings between 300 and 1,500 watts. Commercial models may reach much higher outputs.
You can convert between these units using a simple formula:
1 watt ≈ 3.41 BTUs per hour
This conversion helps you compare different models and ensures you choose a heater that matches your room’s requirements. Always check the manufacturer’s label for these details before making a decision.
Matching Infrared Heater Output to Room Size
The size of your room directly affects the amount of heating power you need. Larger rooms require more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature. Ceiling height, insulation, and the presence of windows also influence your choice. Industry studies and fire safety standards provide benchmarks for matching heater output to room dimensions. The table below summarizes findings from several standardized tests:
| Test Standard / Organization | Room Dimensions (m) | Ignition Source / Burner Output (kW) | Notes / Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| NORDTEST (1986) | 2.4 × 3.6 × 2.4 | 100 kW ignition source; escalates to 300 kW if no ignition | Uses a room similar to ASTM; burner outputs tested at 40, 160, 300 kW; 160 or 300 kW acceptable ignition levels |
| VTT Finland Study | ~2.4 × 3.6 × 2.4 (chipboard-lined room) | Burners of 40, 160, 300 kW tested | No significant difference among burner sizes; difference between 40 and 160 kW larger than between 160 and 300 kW |
| ASTM Proposed Method (1982) | 2.4 × 3.7 × 2.4 | Standard ignition burner output: 176 kW | Burner placed in rear corner; method withdrawn but variants still used; complex exhaust requirements |
Note: These benchmarks relate to gas burner outputs in fire safety tests. For everyday infrared heating, you should use manufacturer recommendations and calculators for more practical guidance.
Using Calculators and Manufacturer Guides
You can simplify the process of sizing your infrared heater by using online calculators and manufacturer guides. Heatingpoint.com provides an Infrared Panels Buying Guide with a calculator that estimates the wattage you need based on your room’s area. This tool recommends choosing a wattage equal to or greater than the suggested value to ensure efficient operation and longer heater life.
Royal Infrared Heating® offers a Heating and Consumption Calculator that considers both room size and insulation quality. This calculator helps you determine the number of heaters required and estimates energy consumption, giving you a clear picture of your heating needs.
Sundirect Heater suggests a straightforward formula: multiply your room’s area in square meters by 70 to find the minimum wattage needed. Their guide also covers heater placement and additional features, helping you optimize heat distribution.
Tip: Always use a calculator or manufacturer guide before purchasing. These resources help you avoid under- or over-sizing your infrared heating system, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency.
Practical Examples for Common Spaces
When you select an infrared heater, you benefit from understanding how real-world spaces use these systems for effective heating. Let’s look at a typical office environment and see how you can apply these insights to your own space.
Consider an L-shaped office with a volume of 70 cubic meters. In this scenario, two ceiling-mounted infrared panels—one rated at 750W and another at 600W—provide a combined nominal power of 1350W. This setup delivers about 20 watts per cubic meter, which aligns with industry recommendations for efficient heating in offices with average insulation.
| Parámetro | Details / Values |
|---|---|
| Room Volume | 70 m³ (L-shaped office) |
| Heater Panels Installed | 750W + 600W ceiling-mounted IR panels |
| Combined Nominal Power | 1350W (20W/m³) |
| Initial Energy Surge | ~1880W for 2-3 seconds, then stabilizes |
| Energy Usage (Efficient Trial) | 0.556 kWh/h over 8.25 hours |
| Comfort Factor (ASHRAE) | -0.5 to +0.5 (optimal comfort and efficiency) |
| Building Insulation | Poor (U-value ~2.3-2.5 W/m²/K) |
| Ventilation | Two doors ajar (~30mm gap each) |
You notice that the panels heat the room quickly, with a brief power surge at startup. After this, the system stabilizes and maintains a comfortable temperature. Even with poor insulation and constant ventilation, the heating remains effective. You can dial down the power during the day to save energy, which keeps the wall temperature below 20°C for best efficiency.
Tip: Compact infrared panels allow you to adjust heating output easily. This flexibility helps you maintain comfort while reducing energy costs, especially in spaces with variable occupancy or insulation quality.
In your own home or office, you can use similar calculations. Measure your room’s volume, then multiply by 20W to estimate the required power for infrared heating. For example, a 30 m³ bedroom would need about 600W. Always consider insulation and ventilation, as these factors influence how much heating you need.
You gain several benefits from this approach:
- Rapid heat-up times
- Consistent comfort, even with open doors or older buildings
- Simple controls for dialing down power and saving energy
By following these practical examples, you ensure your infrared heating system matches your space and delivers reliable performance.
Step 4: Consider Essential Features When You Choose the Right Heater
When you select an infrared heater, you should focus on features that enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience. These essential elements help you maximize comfort while minimizing risks and operating costs.
Safety Features for Infrared Heaters
Safety remains a top priority when choosing any heating device. Modern infrared heaters include several built-in protections that reduce the risk of accidents and ensure reliable operation.
Tip-Over Protection
Tip-over protection uses a sensor to detect if the heater falls or tilts beyond a safe angle. When this happens, the heater instantly shuts off power, preventing fire hazards. TÜV, UL, and ETL certifications confirm that these systems have passed rigorous safety tests. You can trust that a heater with these certifications will respond quickly and reliably in case of an accident.
Overheat Shut-Off
Overheat shut-off relies on a thermostat-controlled system. If the heater’s internal temperature exceeds a safe threshold, it automatically powers down. This feature prevents overheating and reduces the risk of fire. High-quality infrared heaters often include this protection, and certifications like UL and ETL indicate that the device has undergone extensive testing for electrical and fire safety.
Automatic shut-off systems, similar to those used in medical infrared devices, help prevent thermal injury by limiting surface temperatures. These principles translate well to home heating, offering you peace of mind during extended use.
Cool-Touch Exteriors
Cool-touch exteriors keep the outer surfaces of the heater safe to touch, even during operation. This design protects you and your family from accidental burns. If you have children or pets, this feature becomes especially important. Manufacturers often highlight this benefit in their product descriptions, so look for it when comparing models.
| Safety Feature | Cómo funciona | Certification/Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Tip-Over Protection | Shuts off if the heater tips or falls | TÜV, UL, ETL |
| Overheat Shut-Off | Powers down if temperature exceeds safe limit | UL, ETL |
| Cool-Touch Exterior | Keeps surfaces safe to touch during operation | Manufacturer specification |
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
You want a heater that delivers warmth without driving up your energy bills. Energy-efficient infrared heaters convert nearly all input electricity into usable heat, making them a strong choice for targeted comfort. However, simulation studies show that while these heaters offer high heating efficiency, heat pumps still outperform them in long-term energy savings and cost-effectiveness. Heat pumps provide three to four units of heat per unit of electricity, but they require higher upfront investment.
A large-scale trial in Alberta demonstrated that using infrared imaging to identify heat loss in homes led to an average 0.8% reduction in natural gas use. Households that received personalized heat loss reports achieved up to 8.1% savings per $100 of estimated annual savings. These results suggest that combining infrared heating with building envelope improvements can significantly boost energy efficiency.
For best results, choose a heater certified to ANSI Z83.19 or similar standards. These certifications ensure both safety and energy efficiency, supporting your goal of reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Controls and Programmable Settings
User-friendly controls and programmable settings allow you to tailor heating to your schedule and preferences. Many models offer digital thermostats, remote controls, and timers. You can set the heater to turn on before you arrive home or shut off automatically at night. Advanced features, such as smart home integration, let you adjust settings from your phone or voice assistant.
- Digital thermostats provide precise temperature control.
- Timers and scheduling features help you avoid unnecessary energy use.
- Remote controls and smart integration add convenience and flexibility.
When you evaluate these essential features, you ensure that your infrared heater meets your safety, efficiency, and comfort needs.
Noise Level and Design
When you select an infrared heater, you want a model that fits your environment both visually and acoustically. Noise level plays a significant role in comfort, especially if you plan to use the heater in bedrooms, offices, or quiet living spaces. Many modern infrared heaters operate quietly, but some models include fans or moving parts that can generate noticeable sound.
TechGearLab performed objective sound testing on a range of space heaters, including infrared models. They used a professional sound level meter to record decibel levels. Their results show that the Dreo Atom One stands out as the quietest heater tested, producing only 39.3 dBa. In comparison, the GiveBest Ceramic heater registered a higher noise level at 47.7 dBa. The Dr. Infrared DR-968, a popular infrared model, features variable fan speeds that help maintain consistent warmth. While the exact decibel value for the DR-968 was not specified, reviewers describe its operation as similar to the gentle hum of a refrigerator. This makes it suitable for environments where low noise is essential.
You should also consider design when choosing an infrared heater. A well-designed heater blends with your décor and meets your functional needs. Consumer reviews highlight several models for their design features and usability:
- Dr. Infrared DR-968: Users appreciate its retro look, portability with wheels, and quiet operation. Some mention variability in build quality and lifespan.
- Heat Storm models: These heaters offer design-forward options, such as wood grain finishes and easy portability. Some users note differences in fan noise, especially when moving the unit on wheels.
- Duraflame Electric Logs heater: This model receives praise for its decorative appearance and multiple temperature and lighting settings. It works well in small rooms and adds visual appeal.
- Dr. Heater DR-238: Designed for outdoor use, this heater features a waterproof aluminum exterior and remote control. Some users find the 6-foot cord limiting for placement flexibility.
Tip: When you compare infrared heaters, check for both noise ratings and design features. A quiet heater with a style that matches your space will enhance your comfort and satisfaction.
The table below summarizes key design and noise considerations for popular infrared heater models:
| Modelo | Notable Design Features | Noise Level (User Feedback) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Infrared DR-968 | Retro look, wheels, compact | Quiet, fridge-like hum | Bedrooms, offices |
| Heat Storm | Wood grain, portable | Varies with fan/wheel use | Living rooms, small spaces |
| Duraflame Electric Logs | Decorative, lighting options | Quiet, ambient | Small rooms, décor |
| Dr. Heater DR-238 | Waterproof, remote control | Not specified | Outdoor, patios |
You gain the most value by selecting a heater that meets your expectations for both sound and style. Quiet operation ensures minimal disruption, while thoughtful design enhances the look and feel of your space. Always review product specifications and user feedback to make an informed decision.
Step 5: Review Installation and Maintenance for Infrared Heaters
Installation Requirements by Heater Type
Proper installation ensures your infrared heater operates safely and efficiently. You must follow both manufacturer instructions and local codes for every heater type. The Nevada Mechanical Code 2018 and ANSI standards require you to install listed infrared heaters according to their official listing and the manufacturer’s manual. These documents outline specific requirements for support, suspension, and clearances from combustibles. You also need to consider combustion and ventilation air, as well as exhaust openings for gas-powered models.
- Always mount your heater at a height that allows infrared rays to cover the intended area. For example, in bathrooms, position the heater so it distributes warmth evenly.
- Select the correct wattage for your room size. Use low-wattage models for small spaces and higher wattage for larger areas.
- Securely attach wall-mounted or ceiling-mounted units. Avoid using extension cords to reduce fire risk.
- For commercial garages or aircraft hangars, follow special code sections and use only listed heater types.
Tip: Manufacturer installation manuals contain mandatory requirements. Never skip these steps, as they ensure both safety and optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Routine maintenance extends the life of your infrared heater and keeps it running efficiently. You should establish a preventive schedule that includes both visual checks and technical monitoring.
- Clean your heater regularly with a soft, dry cloth. This removes dust and debris without damaging the unit.
- Take baseline thermal images of your heater under normal conditions. Use these images for future comparisons.
- Inspect your heater with an infrared camera to detect temperature anomalies. This helps you spot early signs of wear or failure.
- Monitor key components, such as motor bearings and gaskets, by comparing current and baseline thermal images.
- Set alarm temperature thresholds. If you notice significant changes, schedule maintenance immediately.
- Combine infrared data with other maintenance tools, such as vibration analysis or lubrication checks, for a complete picture.
- Keep a database of temperature readings and thermal images. Analyze trends to optimize inspection intervals.
| Resource Type | Description | Usefulness |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Data | Warm-up/cool-down curves, heater specs | Helps plan maintenance timing |
| Wiring Diagrams | Detailed wiring for various models | Supports safe installation and repairs |
| Guides | Selection and maintenance planning | Assists in choosing and caring for heaters |
| Catalog PDFs | Centralized technical and maintenance info | Reference for performance and upkeep |
Regular maintenance not only prevents breakdowns but also improves energy efficiency and safety.
Warranty and Customer Support
A strong warranty and responsive customer support give you peace of mind. Most reputable manufacturers offer warranties that cover defects in materials and workmanship. You should review the warranty terms before purchasing. Look for coverage on both parts and labor, and check the duration—many warranties last one to three years.
- Register your heater with the manufacturer after purchase. This step ensures you receive full warranty benefits.
- Keep your purchase receipt and installation records. These documents help if you need to file a claim.
- Contact customer support for troubleshooting, replacement parts, or technical questions. Many companies provide online resources, phone support, and downloadable manuals.
A reliable warranty and accessible support team protect your investment and help you resolve issues quickly.
By following proper installation guidelines, maintaining your heater regularly, and understanding your warranty, you ensure safe, efficient, and long-lasting performance from your infrared heating system.
Making Your Final Choice: How to Choose the Right Heater
Comparing Top Infrared Heater Models and Brands
When you reach the final stage of your search, you need to compare the best infrared heater models and brands using clear criteria. Focus on safety certifications, EMF emissions, material quality, and environmental impact. Industry investigations have evaluated over 200 infrared heaters, including portable and full-spectrum models. Brands that lack certifications, use high EMF technology, or rely on environmentally harmful materials often receive lower ratings. You should prioritize models that provide third-party safety certifications and transparent EMF testing. Some manufacturers address EMF concerns through rigorous testing and certifications, which can give you peace of mind. The best infrared heater for your needs will combine low EMF emissions, safe materials, and a strong reputation for reliability. Full-spectrum models offer near, mid, and far infrared wavelengths, which can enhance comfort and health benefits. You also want to consider installation ease and the ability to fit your space. By focusing on these factors, you can confidently narrow your choices to the best infrared heater options available.
Reading Reviews and User Experiences
You gain valuable insights by reading reviews and user experiences before making your purchase. Look for patterns in feedback about performance, durability, and ease of use. Many users highlight the importance of safety features and energy efficiency when selecting the best infrared heater. Reviews often mention how quickly a heater warms a space and whether it maintains consistent comfort. Pay attention to comments about noise levels and design, especially if you plan to use the heater in a bedroom or office. Some users discuss installation challenges or praise models that offer simple setup. You should also check for feedback on customer support and warranty service. Reliable brands tend to receive positive remarks for responsive support and honoring warranties. By considering a range of user experiences, you can identify the best infrared heater that aligns with your expectations and needs.
Setting a Budget and Finding the Best Value
You want to find the best infrared heater that fits your budget while delivering strong performance. Infrared heaters offer up to 30% higher energy efficiency than traditional systems, which helps reduce your long-term costs. These heaters convert nearly all consumed energy into heat, minimizing waste. If you integrate your heater with solar panels, you can cut annual electricity use for heating by about 25%. Studies show that combining infrared heating with solar panels is more cost-effective than other electric solutions when you consider capital expenses. Compact designs lower installation and facility integration costs, and specialized components may increase upfront costs but often lead to lower maintenance expenses. When you evaluate the total cost of ownership, include installation, training, warranty, and maintenance. To optimize your price-performance ratio, assess the size, power, control options, warranties, and energy efficiency ratings of each model. The best infrared heater for your situation will balance upfront investment with long-term savings and reliable operation.
Tip: Always compare the total cost of ownership, not just the purchase price, to ensure you select the best infrared heater for your needs.
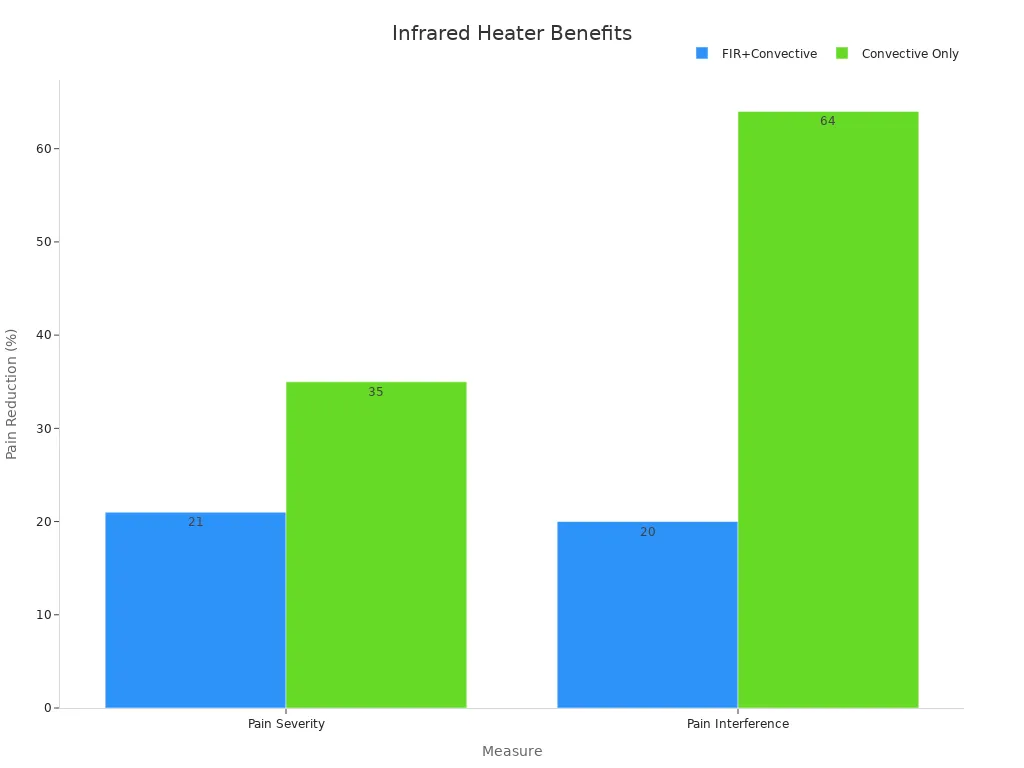
You now have a clear path to select the ideal infrared heater. Assess your space, choose the right type, calculate heating power, review features, and consider installation. Studies show that heat therapy, including infrared heaters, reduces pain severity and interference over time.
| Measure | Treatment Group | % Reduction in Pain |
|---|---|---|
| Pain Severity | FIR + Convective | 21% |
| Pain Severity | Convective Only | 35% |
| Pain Interference | FIR + Convective | 20% |
| Pain Interference | Convective Only | 64% |
With the right heater, you gain comfort, efficiency, and peace of mind for your home or business.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What size infrared heater do you need for your room?
You should calculate the room’s square footage and match it to the heater’s wattage. Most manufacturers provide sizing charts. For example, a 1500-watt heater typically covers up to 150 square feet.
Are infrared heaters safe for children and pets?
Modern infrared heaters include safety features like tip-over protection and cool-touch exteriors. You should always supervise use around children and pets. Place the heater in a stable location away from high-traffic areas.
Can you use an infrared heater as your main heat source?
You can use infrared heaters as a primary heat source in small, well-insulated spaces. For larger or poorly insulated areas, use them as supplemental heating for best results.
How much electricity does an infrared heater use?
Infrared heaters convert nearly all electricity into heat. A 1500-watt unit uses 1.5 kWh per hour. You can estimate your monthly cost by multiplying usage hours by your local electricity rate.
Do infrared heaters dry out the air?
Infrared heaters do not reduce humidity. They heat objects and people directly, so you maintain comfortable air moisture levels. This feature benefits allergy sufferers and helps prevent dry skin.
What maintenance does an infrared heater require?
You should dust the exterior regularly and check for obstructions. Inspect wiring and connections annually. For gas models, schedule professional servicing. Always follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines.
Can you mount an infrared heater on the ceiling?
Many infrared heaters offer ceiling-mount options. You should follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions for safe and effective operation. Ceiling mounting saves floor space and distributes heat evenly.
Are infrared heaters energy efficient compared to other types?
Infrared heaters deliver targeted warmth and minimize energy waste. You often see up to 30% higher efficiency than traditional convection heaters. For maximum savings, choose a model with programmable controls and use it in well-insulated spaces.


