
Halogen heaters have become a staple in modern homes due to their efficient Elemento calefactor and advanced design. These household appliance heating elements, often produced by Jinzhong Electric Heating and other leading Heating element manufacturers, deliver rapid warmth and consistent comfort. Consumers highlight several key benefits:
- High efficiency with instant heat provision
- Low running costs and minimal maintenance
- Portability and ease of installation
Halogen heaters stand out as a practical solution for daily heating needs, offering energy-efficient technology and reliable performance.
Halogen Heaters Explained

What Are Halogen Heaters?
Halogen heaters represent a specialized category of electric heaters that utilize halogen bulbs as their primary heating element. These devices rely on halogen heat to deliver rapid and targeted warmth. Manufacturers design halogen heaters to maximize efficiency and durability, making them suitable for a wide range of environments. The sealed quartz tube, tungsten wire, and inert gas filling distinguish halogen heaters from other electric heating technologies.
How Halogen Heaters Work
Halogen heaters generate halogen heat by passing an electric current through a tungsten filament housed inside a sealed quartz tube. The filament heats up due to electrical resistance, a process known as Joule heating. As the filament reaches high temperatures, it emits infrared radiation. This radiant energy travels through the air and directly warms objects and people in its path, rather than simply heating the surrounding air. The glass envelope and integrated reflector focus the halogen heat forward, increasing the effectiveness of the heater. This method of heat generation allows halogen heaters to provide instant heat and maintain high energy efficiency.
Halogen heaters convert electrical energy into infrared heat, which is absorbed by surfaces and individuals, resulting in immediate comfort.
Key Components and Features
The following table highlights the main components that set halogen heaters apart from other electric heaters:
| Component/Feature | Halogen Heater | Quartz Heater | Carbon Fiber Heater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shell | Sealed quartz glass tube | Quartz glass tube (not sealed) | N/A |
| Elemento calefactor | Tungsten wire inside the sealed tube | Heating wire (not sealed) | Carbon fiber heating body |
| Gas Filling | Filled with inert shielding gas | No inert gas filling | N/A |
| Heating Speed | Fast heating | Moderate heating speed | N/A |
| Light Emission | Visible and near-infrared light (0.75-3.5 µm) | Brightness higher than halogen | Far infrared radiation |
| Durability/Service Life | Over 3000 hours, high thermal efficiency | Shorter life due to oxidation | Alta eficacia |
| Cost | Slightly more expensive | Less expensive | N/A |
Halogen heaters use a sealed quartz tube filled with inert gas to protect the tungsten filament and extend service life. The combination of these components ensures reliable halogen heat output and consistent performance.
Everyday Benefits of Halogen Heaters
Instant and Direct Heat
Halogen heaters deliver instant heat as soon as they are switched on. The halogen bulbs reach operating temperature almost immediately, allowing users to feel warmth within seconds. The radiant halogen heat travels in straight lines, directly warming objects and individuals in its path. A reflector behind the bulb focuses the heat forward, enhancing the direct heating effect. The quartz tube provides a protective barrier while allowing infrared radiation to pass through efficiently.
- Halogen bulbs reach operating temperature almost instantly.
- Radiant heat warms objects directly, not just the air.
- Reflectors enhance direct heating.
- Quartz tubes protect users from direct contact.
Halogen heaters provide instantaneous comfort, making them ideal for spot heating and small spaces.
Energy Efficiency
Halogen heaters excel in energy efficiency due to their ability to convert over 90% of electrical energy into infrared heat. The low thermal mass of the quartz heating tubes enables rapid response times and minimizes energy waste. By warming objects and people directly, halogen heaters reduce the need to heat entire rooms, which lowers overall energy consumption. This targeted approach to halogen heat generation supports cost-effective operation and sustainable energy use.
Halogen heaters offer high energy efficiency by focusing heat where it is needed most, reducing unnecessary power usage.
The benefits of halogen heaters include rapid heating, direct warmth, and efficient energy utilization. These features make halogen heaters a practical choice for everyday comfort and convenience.
How Halogen Heaters Work
Halogen Bulbs and Infrared Radiation
The Science Behind Halogen Heating
Halogen heaters use halogen bulbs to generate halogen heat. These bulbs contain a tungsten filament inside a sealed quartz tube filled with inert gas. When electricity passes through the filament, it heats up and emits electromagnetic energy. Most of this energy leaves the filament as infrared radiation, which is the main source of halogen heat in these devices.
Infrared radiation from halogen bulbs transfers energy directly to objects and people. This process allows halogen heat to warm surfaces quickly and efficiently. Unlike traditional heating methods, halogen heat does not rely on warming the air first. Instead, it delivers warmth straight to the target, reducing energy loss and increasing comfort.
The typical lifespan of halogen bulbs used in halogen heaters ranges from 2,250 to 3,500 hours. This durability surpasses that of standard incandescent bulbs, which usually last between 750 and 1,000 hours. The following table compares the lifespans of different bulb types:
| Bulb Type | Lifespan (hours) |
|---|---|
| Halogen Bulbs | 2,250 – 3,500 |
| Incandescent | 750 – 1,000 |
Halogen bulbs in heaters often last about 2,000 hours, which means users can expect reliable halogen heat for over a year with regular use.
Radiant vs. Convection Heat
Halogen heaters produce radiant heat, while many other electric heaters, such as infrared heaters, may use convection. Radiant halogen heat travels in straight lines and warms objects directly. Convection heaters, on the other hand, heat the air, which then circulates to warm the room.
- Radiant halogen heat provides immediate warmth to people and surfaces.
- Convection heat takes longer, as it depends on air movement.
- Halogen heat reduces energy waste by focusing warmth where it is needed.
Some halogen heaters use infrared reflective coatings to prevent heat escape, further improving efficiency. This technology allows the filament to run hotter, increasing both visible light and halogen heat output.
Safety and Usability Features
Built-In Safety Mechanisms
Manufacturers design halogen heaters with multiple safety features to protect users. Overheat protection automatically shuts off the heater if it gets too hot, preventing fire hazards. Shatter-resistant quartz tubes minimize the risk of injury from broken glass. Many models include UV-absorbing glass filters to reduce ultraviolet exposure.
Additional safety features include secure lamp holding to prevent dislodging, external fuses for electrical safety, and clear labeling for wattage and voltage. Certification from recognized bodies, such as UL or TUV, confirms compliance with strict safety standards.
Tip: Always check for certification labels and follow installation guidelines to maximize safety.
User-Friendly Controls
Halogen heaters offer simple and intuitive controls. Users can adjust power settings, select oscillation modes, or set timers with ease. Clear indicators and labeled switches help prevent misuse. These user-friendly features make halogen heaters accessible for all age groups.
Proper installation and ventilation further enhance safety. Manufacturers recommend placing halogen heaters on stable surfaces and away from flammable materials. These guidelines ensure that halogen heat remains both effective and safe in daily use.
Halogen Heaters vs. Infrared Heaters
Key Differences in Heating Technology
Heat Output and Distribution
Halogen heaters and infrared heaters both use radiant technology, but their heating mechanisms differ significantly. Halogen heaters rely on quartz elements that reach high temperatures and emit halogen heat as near-infrared radiation, which overlaps with visible light. This process creates a noticeable red or orange glow and delivers intense, immediate warmth. The heat feels hot on the skin but is less easily absorbed by the body. In contrast, infrared heaters, such as ceramic models, emit far-infrared radiation with longer wavelengths and lower frequencies. This type of heat feels gentler and is more readily absorbed by the body, providing a comfortable and sustained warmth without visible light.
Halogen heaters operate at surface temperatures around 750°F to 775°F, producing intense, directional halogen heat. Their sealed luminous heat pipes, filled with halogen gas and tungsten filaments, ensure high thermal efficiency and long service life. These heaters typically consume between 900 and 1200 watts, making them suitable for small rooms or targeted areas. Advanced models may offer features like oscillation or humidification, but the core technology remains focused on rapid, direct halogen heat.
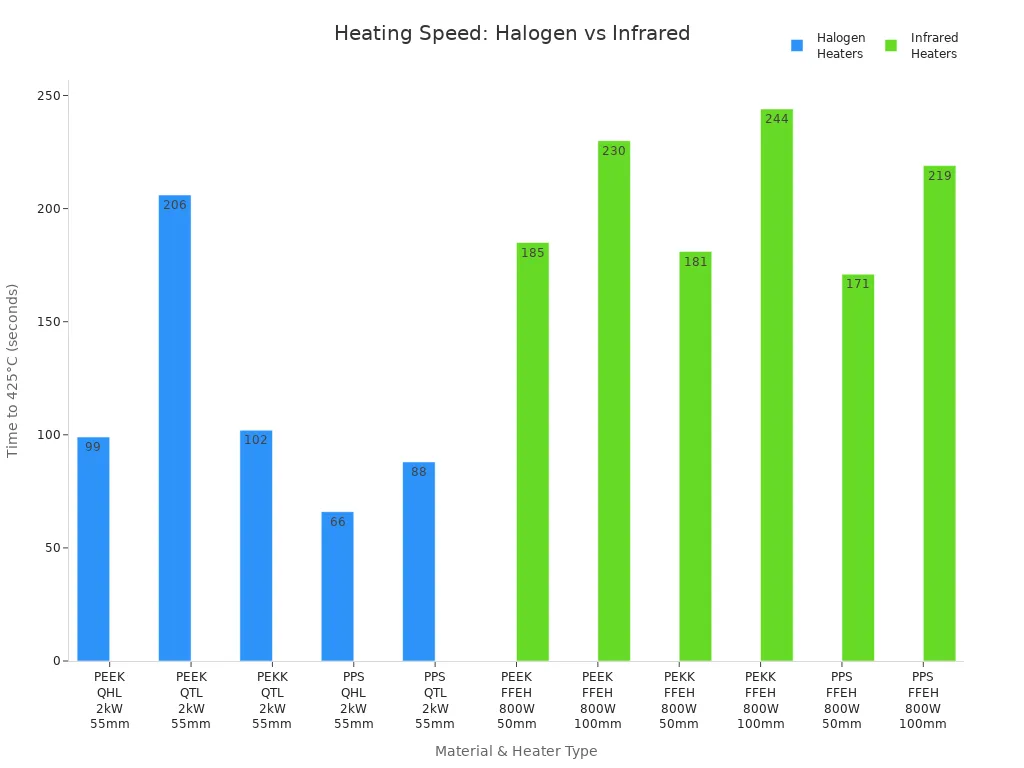
Standardized tests show that halogen heaters heat materials faster than many infrared heaters at similar distances. For example, a 2kW quartz halogen heater can bring certain materials to 425°C in less than 100 seconds, while black hollow infrared elements take longer but provide more uniform surface temperatures and higher peak values when placed closer. The following table summarizes these findings:
| Material | Heater Type & Power | Distance from Material | Time to Reach 425°C (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEEK | 2kW Tungsten Halogen (QHL) | 55mm | 99 |
| PEEK | 800W Black Hollow Infrared (FFEH) | 50mm | 185 |
| PPS | 2kW Quartz Halogen (QHL) | 55mm | 66 |
| PPS | 800W Black Hollow Infrared (FFEH) | 50mm | 171 |
Energy Consumption
Halogen heaters and infrared heaters both offer strong energy efficiency, but their consumption patterns differ. Halogen heaters convert a high percentage of electrical energy into halogen heat, delivering rapid warmth with minimal waste. However, their intense output can lead to higher running costs if used for extended periods, especially in winter. Infrared heaters, particularly those using ceramic elements, often provide slightly better energy efficiency in maintaining comfortable temperatures over time. They achieve this by emitting far-infrared radiation that is more easily absorbed by the body, reducing the need for constant high output.
Pros and Cons of Halogen Heaters
When to Choose Halogen Heaters
Halogen heaters excel in scenarios requiring immediate, focused halogen heat. They are ideal for spot heating in workspaces, reading nooks, or poorly insulated rooms where heating the air is inefficient. Their rapid heat output and portability make them suitable for quick, short-term use. Halogen heaters also offer eco-friendly operation, producing no smoke or carbon monoxide emissions. Built-in safety features, such as auto shut-off and cool-to-touch surfaces, enhance user protection. Easy installation and lightweight design allow users to move these heaters between rooms as needed.
Limitations to Consider
Despite their advantages, halogen heaters have some limitations. The front part of the heater can become hot, posing a burn risk, especially for children and pets. Halogen heat intensity diminishes over distance, making these heaters less effective for large rooms or whole-house heating. Prolonged use can increase electricity costs, reducing their cost-effectiveness in continuous operation. Halogen heaters work best for targeted, immediate warmth rather than sustained, whole-room comfort.
Note: Halogen heaters provide rapid, direct halogen heat, but users should exercise caution with placement and duration of use to maximize safety and efficiency.
Halogen Heaters Compared to Other Heater Types
Halogen Heaters vs. Quartz Heaters
Performance and Use Cases
Halogen heaters and quartz heaters both deliver radiant heat, but their internal designs create differences in performance. Quartz heaters use a coiled wire heating element inside or around a quartz tube. This quartz tube allows nearly all generated infrared heat to pass directly to the target. As a result, quartz heaters provide fast, focused heating and high energy efficiency. Many industrial settings prefer quartz heaters for their ability to deliver intense, targeted warmth with minimal energy loss.
Halogen heaters, on the other hand, use metal heating wires as their core element. While they also provide rapid heat, the construction and materials differ from quartz heaters. This leads to variations in heating efficiency and the way heat is transmitted. Halogen heaters excel in spot heating and small spaces, making them suitable for home and office use where immediate warmth is needed.
Efficiency and Cost
Quartz heaters generally offer higher radiative energy efficiency, especially at elevated filament temperatures. Some quartz tungsten halogen lamps reach up to 95% efficiency, converting almost all electrical energy into usable infrared heat. This efficiency makes quartz heaters a strong choice for applications that demand quick, powerful heating.
When considering cost, quartz heaters usually have a lower upfront price and longer-lasting bulbs. This reduces maintenance expenses over time. Halogen heaters often cost more initially and may require more frequent bulb replacements. However, they can be more energy-efficient during extended use, which may lower running costs for users who need consistent heating. The choice between these two heater types depends on whether the user values lower initial and maintenance costs or prefers energy savings during prolonged operation.
Halogen Heaters vs. Oil-Filled and Ceramic Heaters
Heat Direction and Room Coverage
Halogen heaters emit one-directional heat that targets objects and people directly. This design provides rapid, focused warmth but limits the area covered. They work best for spot heating, such as warming a person sitting at a desk or a small section of a room.
Oil-filled heaters operate differently. They heat oil sealed inside the unit, which then radiates warmth steadily into the room. This process creates consistent, non-directional heat suitable for smaller rooms, but it takes longer to reach the desired temperature. Ceramic heaters use heated ceramic plates. Models with fans push warm air throughout the space, improving room coverage and heat distribution. Fanless ceramic heaters heat more slowly and are better for small areas.
Tip: Choose halogen heaters for instant, targeted warmth. Select oil-filled or ceramic heaters for ambient, whole-room comfort.
Electricity Usage and Comfort
The following table compares the typical power usage and heating behavior of each heater type:
| Heater Type | Power Usage Characteristics | Heating Behavior and Efficiency Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Halogen | Typically lower wattage (e.g., ~400W) | Provides instant radiant heat, effective for short-term, direct heating; power usage is lower for quick heating needs. |
| Oil-filled | Rated around 1500-2000W, steady-state ~800W | Slower to heat up due to thermal mass; provides stable, convection-based heat; continues to emit heat after turning off. |
| Ceramic | Not specified | Generally similar efficiency as other electric resistance heaters; fan models improve room coverage. |
All electric resistance heaters convert electricity to heat at nearly 100% efficiency. Actual electricity usage depends on the wattage and how long the heater runs. Halogen heaters use less power for quick, direct heating, while oil-filled and ceramic heaters consume more energy to maintain ambient warmth over time.
Everyday Advantages of Halogen Heaters
Rapid Heating and Immediate Comfort
Quick Warm-Up for Small Spaces
Halogen heaters excel at delivering instant heat, making them highly effective for small rooms and confined areas. The technology behind these heaters relies on infrared radiation, which targets objects and people directly. Users experience warmth almost immediately after switching on the device. Unlike convection heaters that require time to warm the air, halogen heaters provide a sensation of comfort within seconds. This rapid response proves especially valuable during cold mornings or in spaces that need quick temperature adjustments. The ability to feel warmth instantly sets halogen heaters apart from many other portable heating solutions.
Spot Heating for Individuals
Spot heating represents one of the most practical benefits of halogen heaters. The focused beam of infrared energy allows users to direct warmth precisely where it is needed. Individuals sitting at a desk, reading in a chair, or working in a garage can enjoy targeted comfort without waiting for the entire room to heat up. This approach not only saves energy but also enhances personal comfort. The direct nature of the heat ensures that users remain warm even if the surrounding air remains cool. Halogen heaters offer a reliable solution for anyone seeking immediate, localized warmth.
Safety and Environmental Benefits
No Carbon Monoxide Emissions
Halogen heaters operate using electricity and do not rely on combustion. As a result, they produce no carbon monoxide or other harmful emissions. This characteristic makes them a safer choice for indoor environments, especially in homes with children, elderly individuals, or pets. The absence of fumes or smoke contributes to better indoor air quality and reduces health risks associated with traditional fuel-based heaters. Users can confidently operate halogen heaters in enclosed spaces without concerns about air pollution or ventilation requirements.
Cool-to-Touch Surfaces and Overheat Protection
Manufacturers equip halogen heaters with advanced safety features to minimize risks. Overheat protection uses sensors to monitor the internal temperature. If the heater becomes too hot, the system automatically shuts off power, preventing overheating and potential fire hazards. Cool-to-touch surfaces further enhance safety by keeping the exterior safe, even during extended operation. These design elements significantly reduce the likelihood of burns and accidents, particularly in households with children or pets.
- Cool-touch surfaces keep the heater’s exterior safe to touch, minimizing burn risks.
- Overheat protection uses built-in sensors to automatically shut off the heater if it reaches a dangerous temperature, preventing overheating and fire hazards.
- These features collectively reduce accidents by preventing burns and fires, especially in homes with children or pets.
The combination of these safety features ensures that halogen heaters remain a dependable and secure option for daily use.
Versatility and Portability
Indoor and Outdoor Applications
Halogen heaters demonstrate remarkable versatility, functioning effectively in both indoor and outdoor settings. Their direct infrared heat warms surfaces and people without relying on air temperature, making them suitable for open-air locations and uninsulated spaces. The following table highlights the features that enable halogen heaters to perform well in diverse environments:
| Feature | Explicación |
|---|---|
| Direct Infrared Heat | Heats surfaces and people directly without warming surrounding air, ideal for open-air locations. |
| High Element Temperature | Results in a bright, high output heater suitable for heating from a distance. |
| Wide or Focused Heat Dispersion | Allows flexibility in heating style, either broad comfort or focused warmth from heights. |
| Immediate Heat Response | Infrared heating starts instantly, providing quick warmth upon switching on. |
| Suitable for Uninsulated/Open Areas | Radiant heat warms objects, not air, making it effective outdoors or in non-insulated spaces. |
This adaptability allows users to deploy halogen heaters on patios, balconies, garages, or workshops, as well as in living rooms and bedrooms.
Easy Placement and Movement
Portability stands out as one of the key benefits of halogen heaters. Most models feature lightweight construction and compact designs, enabling users to move them effortlessly from one location to another. The absence of heavy components or complex installation requirements means that individuals can reposition the heater as needed. Whether providing instant heat in a home office during the day or warming a patio in the evening, halogen heaters offer unmatched convenience. Their easy placement and movement contribute to their popularity among users seeking flexible heating solutions.
Tip: Always place halogen heaters on stable surfaces and away from flammable materials to maximize safety and performance.
Halogen heaters combine rapid heating, robust safety features, and versatile applications, making them a practical choice for a wide range of everyday scenarios.
Practical Uses of Halogen Heaters in Daily Life

Home Heating Solutions
Living Rooms, Bedrooms, and Small Spaces
Halogen heaters provide rapid and focused warmth in living rooms, bedrooms, and other small spaces. Their radiant heat targets objects and people directly, making them ideal for spot heating in rooms with high ceilings or poor insulation. Many homeowners use halogen heaters to selectively warm occupied areas, which helps reduce overall heating costs. These heaters operate quietly and do not rely on fans, benefiting individuals with dust allergies. Safety features such as cool cabinets and protective grilles make halogen heaters suitable for homes with children and pets. Users appreciate the instant warmth at the touch of a button, especially during cold mornings or evenings.
- Halogen heaters deliver immediate comfort in small to medium-sized rooms.
- Quiet operation supports a peaceful environment.
- Safety features enhance suitability for family homes.
Garages, Workshops, and Basements
Garages, workshops, and basements often present heating challenges due to poor insulation and large open spaces. Halogen heaters excel in these environments by providing targeted heat where it is needed most. Their energy-efficient design allows users to warm specific zones without wasting energy on unoccupied areas. The direct radiant heat proves effective for individuals working at benches or stations, ensuring comfort during colder months. Safety mechanisms, including overheat protection and sturdy construction, support reliable operation in utility spaces.
Tip: Position halogen heaters near workstations or seating areas to maximize efficiency and comfort.
Office and Commercial Applications
Spot Heating for Desks and Workstations
In office settings, halogen heaters serve as efficient spot heaters for desks and workstations. Their short-wave infrared technology delivers instant, directional heat with approximately 86% energy efficiency. The visible orange glow reassures users that the heater is active. Halogen heaters perform best in targeted zones, providing quick warmth for individuals without disturbing the entire office environment. They offer a practical solution for temporary or mobile workspaces where rapid heating is essential.
Waiting Areas and Reception Spaces
Commercial environments such as waiting areas and reception spaces benefit from the immediate warmth provided by halogen heaters. The following table compares halogen heaters to other common office heating solutions:
| Heater Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halogen Heaters | Instant heat, visible glow | Directional, limited coverage | Targeted zones, reception areas |
| Fan Heaters | Quick warmth, portable | Noisy, circulates dust | Retail, workshops |
| Oil-Filled Radiators | Silent, consistent heat | Slow to warm, heavy | Offices, meeting rooms |
| Ceramic Heaters | Rapid heating, energy efficient | Fan noise in some models | Small offices, reception areas |
Halogen heaters stand out for their ability to provide quick, visible warmth in areas where guests or employees require immediate comfort.
Outdoor and Recreational Use
Patios, Decks, and Balconies
Patio heaters using halogen technology offer fast heat-up times and strong sensations of warmth, making them popular for outdoor spaces like patios, decks, and balconies. These heaters use shortwave infrared radiation to heat people and objects directly, rather than the surrounding air. Users benefit from energy efficiency and minimal maintenance requirements. Safety features such as protective grills and options for wall or ceiling mounting keep patio heaters out of reach, reducing accident risks. Zoned heating allows users to target specific areas, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption.
- Patio heaters provide effective warmth for outdoor dining and gatherings.
- Wall or ceiling mounting options enhance safety and flexibility.
- Zoned heating supports energy savings in large outdoor spaces.
Camping and Travel Scenarios
Halogen heaters also serve recreational needs during camping and travel. Their portability and instant heat make them suitable for temporary shelters, tents, or RVs. Users must select models with appropriate IP ratings to ensure protection against water and dust. High element temperatures require careful installation and use of protective grills. While the visible glow may not suit every setting, halogen heaters remain a reliable choice for outdoor comfort.
Note: Always verify waterproof ratings and use external controllers for safe operation of patio heaters in outdoor environments.
Choosing and Maintaining Halogen Heaters
Selecting the Right Halogen Heater
Room Size and Power Settings
Selecting the appropriate halogen heater for a space requires careful consideration of room size and power output. A small room benefits from a lower wattage model, such as 200 watts, which provides sufficient warmth without excessive energy use. Larger areas demand higher wattage units, often around 800 watts, to ensure effective heating. Users should match the heater’s wattage to the dimensions of the room for optimal comfort and efficiency.
Other important factors include energy ratings and efficiency. Comparing models based on their energy consumption helps users balance heating needs with power usage. Some halogen heaters offer additional features, such as timers or oscillation, which can improve heat distribution and convenience. These features allow users to customize their heating experience and manage energy costs more effectively.
Tip: Always place halogen heaters in well-ventilated areas and avoid confined spaces or locations near combustible materials.
Safety Certifications and Features
Safety remains a top priority when choosing halogen heaters. Models equipped with auto shut-off mechanisms prevent overheating and reduce fire hazards. Users should look for products with recognized safety certifications, such as UL or CE marks, which indicate compliance with industry standards. Protective grills and cool-touch surfaces further enhance user protection, especially in homes with children or pets.
A checklist for safety features includes:
- Auto shut-off for overheating prevention
- Sturdy protective grills
- Cool-touch exteriors
- Clear labeling for wattage and voltage
- Certification from reputable organizations
Regular inspection for wear or damage ensures continued safe operation. Following manufacturer instructions supports both safety and heater longevity.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Cleaning and Longevity
Routine maintenance extends the lifespan of halogen heaters. Dust and debris can accumulate on the heater’s surface and internal components, reducing efficiency. Users should unplug the heater and allow it to cool before cleaning. A soft, dry cloth removes dust from the exterior, while a gentle brush can clear vents and grills. Avoid using water or harsh chemicals, as these may damage electrical parts.
Proper storage during warmer months also preserves the heater’s condition. Storing the unit in a dry, dust-free environment prevents corrosion and mechanical wear. Regular cleaning and careful handling contribute to reliable performance year after year.
When to Replace Your Heater
Even with diligent care, halogen heaters have a finite service life. Signs that indicate replacement include persistent malfunction, visible damage to the quartz tube, or a decline in heating performance. If the heater fails to reach its usual temperature or the safety features stop functioning, users should discontinue use and seek a replacement. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines for replacement intervals ensures continued safety and efficiency.
Note: Regular maintenance and timely replacement protect both users and property, supporting a safe and comfortable environment.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Halogen Heaters
Energy Usage and Cost Myths
Are Halogen Heaters Expensive to Run?
Many people believe that all space heaters consume large amounts of electricity and lead to high utility bills. This misconception often discourages individuals from considering efficient heating options. In reality, halogen heaters operate with lower power output, typically around 1200 watts. This design makes them economical for short-term heating needs.
- Space heaters do not always use excessive electricity.
- Halogen models provide immediate warmth, reducing the time they need to run.
- These heaters rank among the most cost-effective electric heating solutions.
- Using a space heater for a specific room can be more affordable than running central heating for the entire home.
- Proper placement, understanding wattage, and matching the heater to the room size help optimize energy use and cost savings.
- Myths about high energy usage apply to space heaters in general, not specifically to halogen models.
Data supports the idea that halogen heaters offer efficient and affordable operation when used correctly. Users who focus on targeted heating and follow recommended guidelines can manage costs effectively.
Safety Concerns and Fire Risks
Proper Use and Precautions
Safety remains a top priority when using any electrical appliance. Some individuals worry about fire risks or accidents related to portable heaters. Manufacturers address these concerns by equipping halogen models with advanced safety features. Overheat protection, tip-over switches, and cool-to-touch surfaces help prevent accidents.
Users must follow safety precautions to ensure safe operation. These include:
- Placing the heater on a stable, flat surface.
- Keeping the device away from flammable materials such as curtains or papers.
- Never leaving the heater unattended while in use.
- Regularly inspecting the power cord for damage.
- Allowing adequate ventilation around the unit.
Adhering to safety precautions reduces the risk of fire and injury. Reading the manufacturer’s instructions and following all safety precautions ensures reliable performance and peace of mind.
Tip: Always unplug the heater when not in use and store it in a dry, safe location.
Effectiveness in Large Spaces
Can Halogen Heaters Warm Big Rooms?
Some users expect a single portable heater to warm large or open spaces. Halogen models excel at providing rapid, focused heat in small to medium-sized rooms. Their design targets people and objects directly, rather than heating the entire air volume.
In large rooms, the heat may not reach distant areas. The warmth feels strongest near the device and fades with distance. For best results, users should use halogen models for spot heating or in enclosed spaces. Supplementing with additional units or using central heating may be necessary for larger areas.
Note: Understanding the intended use and limitations of halogen models helps set realistic expectations and ensures optimal comfort.
Halogen heaters provide rapid, efficient, and focused warmth for daily environments. Their advanced safety features and adaptable design support use in homes, offices, and outdoor areas. Users benefit from immediate comfort and straightforward operation. By understanding both the strengths and limitations of these devices, individuals can select the most effective heating solution for their specific needs.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
What makes halogen heaters different from other electric heaters?
Halogen heaters use halogen bulbs that emit infrared radiation. This technology provides instant, direct heat to objects and people. Other electric heaters often rely on convection, which warms the air instead of surfaces.
Are halogen heaters safe for use around children and pets?
Manufacturers design halogen heaters with safety features like cool-touch surfaces and overheat protection. Users should always supervise children and pets near any heater and follow all safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
How much electricity does a typical halogen heater use?
Most halogen heaters operate between 400 and 1200 watts. Actual energy consumption depends on the model and usage time. Users can check the product label or manual for specific wattage information.
Can halogen heaters be used outdoors?
Many halogen heaters work well in outdoor settings such as patios or balconies. Users should select models with appropriate weatherproof ratings and always follow manufacturer recommendations for outdoor use.
How often should users clean or maintain a halogen heater?
Regular cleaning improves performance and safety. Users should dust the exterior and vents every few weeks. Always unplug the heater and let it cool before cleaning. Refer to the manual for detailed maintenance instructions.
Do halogen heaters produce any harmful emissions?
Halogen heaters run on electricity and do not burn fuel. They produce no carbon monoxide or other harmful emissions, making them safe for indoor air quality.
What is the average lifespan of a halogen heater bulb?
Halogen heater bulbs typically last between 2,000 and 3,500 hours. Lifespan depends on usage patterns and proper maintenance. Users should replace bulbs when heating performance declines.


